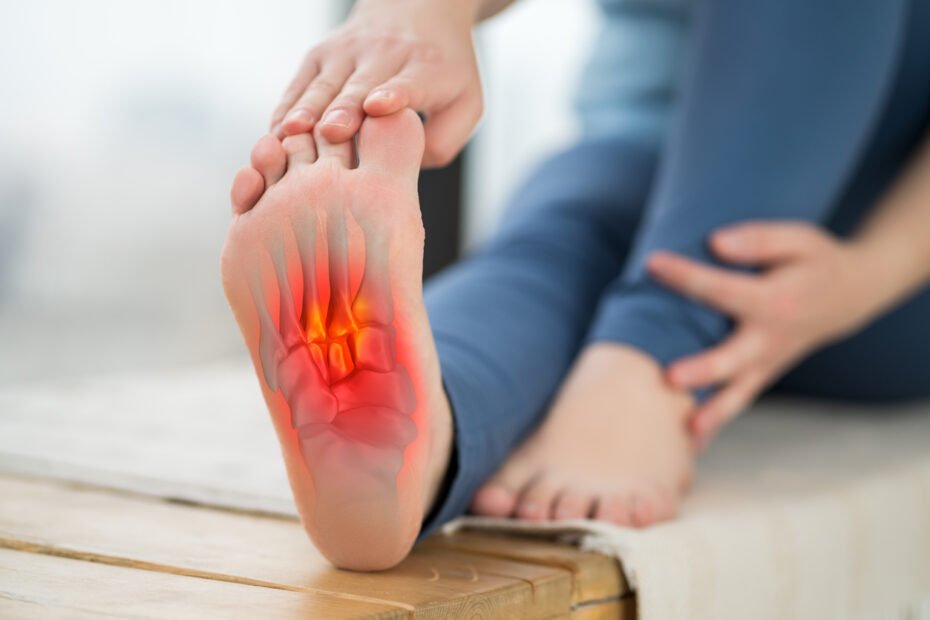
In the dim glow of dawn, as the world awakes to the promise of a new day, John, a passionate runner, sets out on his usual trail. The serene silence, only broken by the rhythmic tap of his shoes, carries him forward. But this morning, the usual joy of his run is marred by a sharp, persistent pain at the base of his foot, a pain that seems to echo with every step he takes. This isn’t just any pain; it’s a signal from his body, hinting at a deeper issue that many like him face: plantar fasciitis, a condition often shadowed by its complex relation with neuropathy. As we delve into this article, we explore the nuances of these conditions, the interconnection, diagnosis, and treatments, aiming to offer solace and solutions to those enduring similar paths as John.
Understanding Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a condition that causes heel pain, specifically on the plantar aspect of the foot. The plantar fascia is a ligament that connects the heel bone to the toes and supports the arch of the foot. When the plantar fascia becomes inflamed or irritated, it can lead to symptoms of plantar fasciitis, one of the most common causes of heel pain. This condition is common and affects people of all ages, although it is more prevalent in adults between the ages of 40 and 60. Understanding the common causes of heel pain, including plantar fasciitis, is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
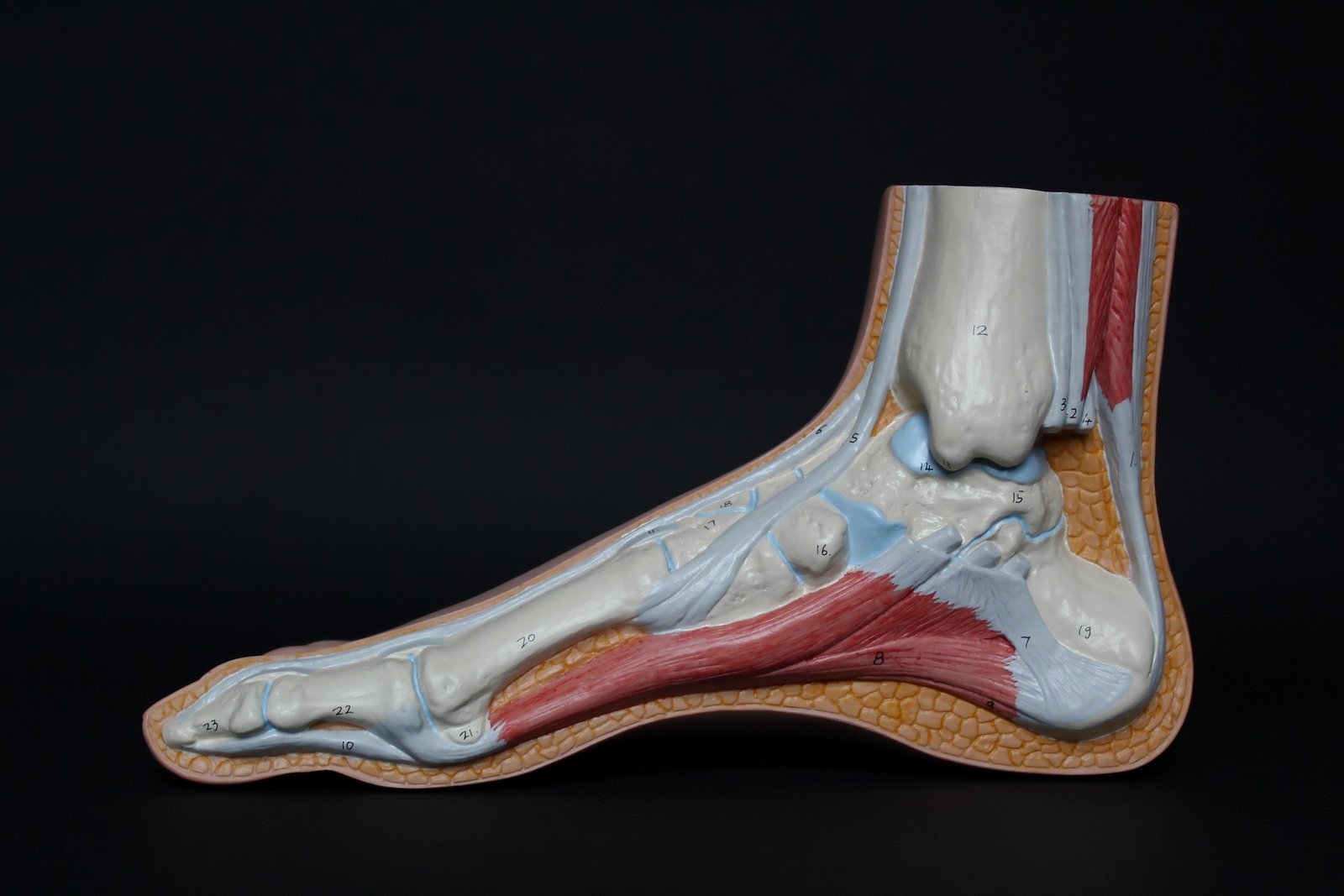
What is Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is the inflammation of the plantar fascia, a ligament that runs along the bottom of the foot, connecting the heel bone or calcaneus to the toes. The plantar fascia plays a vital role in supporting the arch of the foot and absorbing shock during walking and running. When the plantar fascia becomes irritated or damaged, it can lead to heel pain and discomfort, which is the hallmark symptom of plantar fasciitis. This condition is commonly seen in individuals who participate in high-impact activities or have underlying foot conditions such as flat feet or high arches. Understanding the role of the calcaneus and plantar fascia in plantar fasciitis is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The main cause of plantar fasciitis is repetitive strain on the plantar fascia, which can result from activities that put excessive stress on the foot, such as running, jumping, or standing for long periods. Other risk factors that can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis include obesity, flat feet, high arches, tight calf muscles, and wearing improper footwear.
The most common symptom of plantar fasciitis is heel pain, typically located on the bottom of the foot near the heel. The pain may be sharp, stabbing, or throbbing and is often worse in the morning or after long periods of rest. Pain and discomfort may also increase after activities like running or walking for extended periods. Some individuals may experience tenderness and inflammation along the plantar fascia, a heel spur, or pain along the medial aspect of the heel.
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
The primary symptom of plantar fasciitis is heel pain, which can range from mild to severe. The pain is typically felt at the bottom of the foot, near the heel, and is often described as a sharp, stabbing sensation. It may also be accompanied by inflammation and tenderness along the plantar fascia, which can be mistaken for symptoms of Baxter’s neuritis or heel spur syndrome. It is important to properly diagnose the cause of heel pain in order to receive appropriate treatment, as Baxter’s neuritis and heel spur syndrome require different approaches for effective management.
Many people with plantar fasciitis experience the most severe pain with their first steps in the morning or after long periods of rest. This is known as post-static dyskinesia, and it occurs because the plantar fascia tightens and contracts during periods of inactivity, making it more susceptible to strain when pressure is suddenly applied.
In addition, pain and discomfort from plantar fasciitis may worsen after prolonged standing or physical activities that involve the feet, such as running or walking. It may also be aggravated by walking barefoot, on hard surfaces, or on uneven terrain.
It is important to note that the symptoms of plantar fasciitis can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience sharp, stabbing pain, while others may have a dull ache or throbbing discomfort. The severity of the pain can also range from mild to severe, and it may impact daily activities and quality of life.
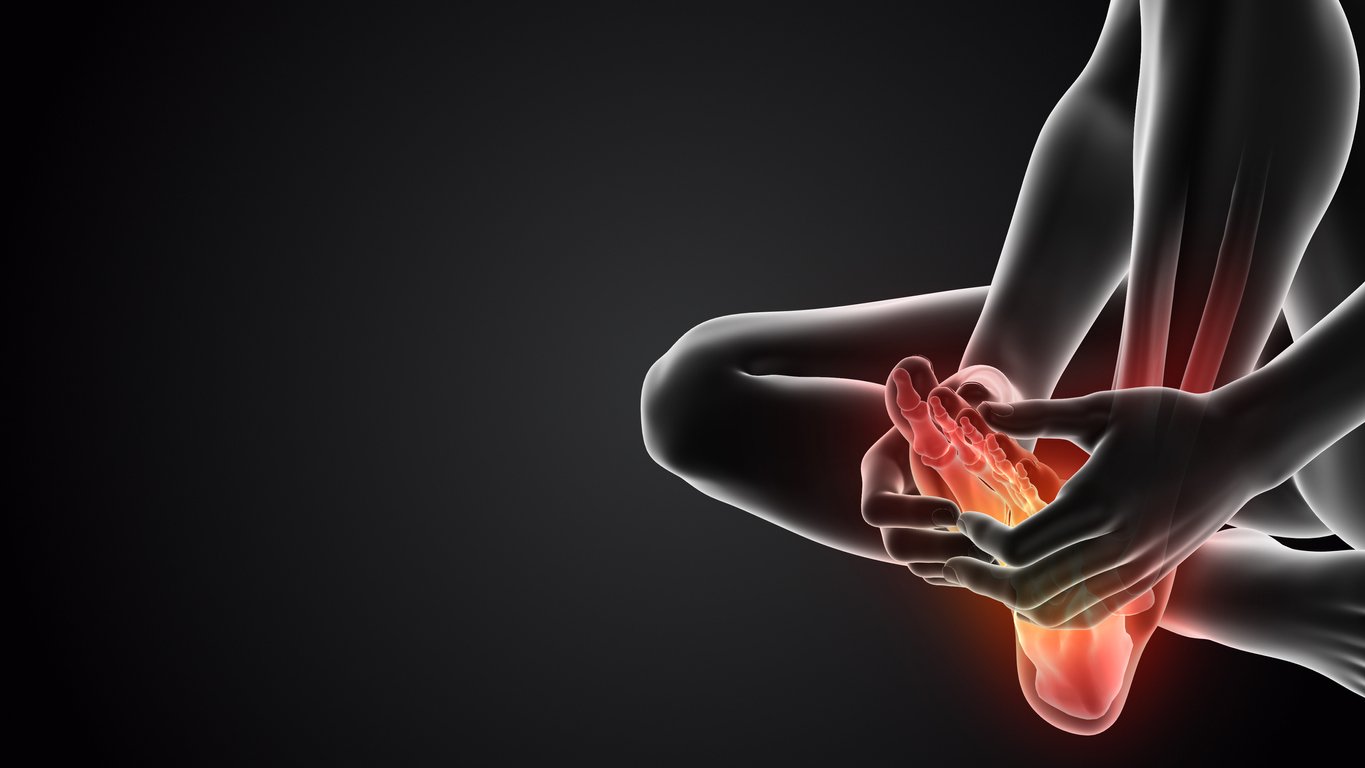
Exploring Neuropathy
Neuropathy is another foot condition that can cause significant discomfort and affect nerve function. It is a condition in which nerve damage interferes with the transmission of signals between the brain and other parts of the body. Neuropathy can result from various causes, including diabetes, infections, exposure to toxins, and certain medical conditions.
Understanding the different types of neuropathy, including polyneuropathy, and their symptoms is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Polyneuropathy, which affects many nerves at once, is the most common form of neuropathy and can cause pain and discomfort.
What is Neuropathy?
Neuropathy is a condition characterized by nerve damage that disrupts the communication between the brain and other parts of the body. It can affect the peripheral nerves, which are responsible for transmitting sensory and motor signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body.
There are different types of neuropathy, but peripheral neuropathy is one of the most common forms. It typically affects the nerves in the hands and feet, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, burning sensations, and muscle weakness.
The causes of neuropathy can vary, ranging from underlying medical conditions like diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and infections to environmental factors such as exposure to toxins and certain medications. Additionally, nerve fibers can become damaged due to compression, inflammation, or physical trauma.
The symptoms of neuropathy can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of nerve damage and the specific nerves affected. Patients may experience numbness, tingling, or a “pins and needles” sensation in the affected areas. They may also have difficulty with coordination, balance, and muscle control, making it challenging to perform everyday tasks.
Symptoms of Neuropathy
Neuropathy can present with a wide range of symptoms, depending on the type of nerves affected and the severity of the damage. Common symptoms of neuropathy include numbness, tingling, burning sensations, and muscle weakness. Patients may also experience discomfort or pain, which can be described as sharp, stabbing, or shooting.
Numbness is often one of the first signs of neuropathy and can occur in the hands, fingers, feet, or toes. It may be accompanied by a loss of sensation, making it difficult to feel touch, temperature changes, or pain. This can increase the risk of injury, as individuals may not be aware when they have a wound or infection.
Tingling and burning sensations, also known as paresthesia, are frequently experienced with neuropathy. Patients may describe these sensations as “pins and needles” or a crawling feeling on the skin.
Muscle weakness is another common symptom of neuropathy, as nerve damage can affect the muscle fibers’ ability to receive signals from the brain. This can result in reduced muscle strength, difficulty with coordination, and overall decreased mobility.
Discomfort or pain is also prevalent in neuropathy and can range in severity from mild to severe. The pain may be constant or intermittent and can be exacerbated by certain movements or activities. It is essential to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of neuropathy to address the underlying causes and manage the associated symptoms effectively.

Relation between Plantar Fasciitis and Neuropathy
When considering foot conditions like plantar fasciitis and neuropathy, it’s essential to understand that they impact distinct areas. Plantar fasciitis primarily involves inflammation of the plantar fascia, whereas neuropathy stems from nerve damage. Despite their differences, individuals with neuropathy may encounter foot pain akin to plantar fasciitis.
Accurate diagnosis plays a critical role in distinguishing between these conditions. Furthermore, concurrent ailments such as diabetes can elevate the susceptibility to both plantar fasciitis and neuropathy.
What links Plantar Fasciitis and Neuropathy?
The connection between Plantar Fasciitis and Neuropathy lies in their shared manifestation of foot pain, each stemming from distinct origins. Neuropathy can lead to secondary Plantar Fasciitis due to altered walking patterns, while existing Plantar Fasciitis may worsen neuropathic symptoms. Collaborative podiatry and neurology care are crucial for dual-diagnosis patients.

Diagnosis of Plantar Fasciitis and Neuropathy
Clinical diagnosis of plantar fasciitis and neuropathy involves thorough evaluation. Physicians conduct a clinical exam, including a physical examination, to assess symptoms like heel pain, tingling, or numbness. Utilizing MRI aids in visualizing structures for pinpointing nerve entrapment. The physical examination should also include the simple thigh and leg raise, which, if painful, may indicate a disorder of the lower back. The examination may reveal issues like tarsal tunnel syndrome or posterior tibial nerve compression, affecting foot and ankle function.
Understanding the involvement of nerve fibers and severity guides treatment planning. Additionally, considering stress fractures or rheumatoid arthritis in the differential diagnosis is crucial for comprehensive care. Incorporating gait analysis and radiographs helps in identifying underlying causes of discomfort.
Clinical Exam for Plantar Fasciitis and Neuropathy
During a clinical examination for plantar fasciitis, healthcare providers evaluate the foot and ankle’s range of motion. Identifying tenderness along the plantar fascia and the medial calcaneal tubercle can be indicative of plantar fasciitis. On the other hand, neuropathy clinical exams focus on assessing sensory deficits, reflexes, and muscle strength.
Physicians may conduct specific maneuvers to provoke symptoms associated with these conditions, such as testing for pain along the plantar aspect of the heel.
A comprehensive clinical assessment, including evaluation of the plantar aspect of the heel, plays a vital role in ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective management of both plantar fasciitis and neuropathy.
Role of MRI in Diagnosis
Utilizing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays a vital role in diagnosing plantar fasciitis and neuropathy accurately. By producing detailed images of soft tissues, MRI helps to pinpoint underlying issues effectively. Moreover, it assists in differentiating between various conditions with similar symptoms, aiding in ruling out other potential causes.
This advanced diagnostic tool is instrumental in devising precise treatment strategies, making it essential for healthcare providers to grasp its significance in facilitating optimal treatment decisions.
Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative treatment options for foot conditions like tarsal tunnel syndrome and nerve entrapment involve non-invasive methods to alleviate pain. These options target the compression of the posterior tibial nerve, also known as tarsal tunnel syndrome, using techniques such as gait analysis and MRI for effective diagnosis.
Foot orthotics and targeted exercises can help address compression of the posterior tibial nerve, reducing symptoms like plantar heel pain. Conditions like stress fractures or rheumatoid arthritis may benefit from treatments focusing on the abductor hallucis muscle and Achilles tendon without surgical intervention, aiding in pain relief and improved ambulation.
Impact of Conservative Care
Patients suffering from foot conditions like plantar fasciitis and neuropathy often find relief through conservative care methods, including the use of orthotic devices. These treatments aim to alleviate symptoms, enhance overall well-being, and potentially eliminate the need for surgical procedures. By effectively implementing conservative therapies, individuals can not only manage existing issues but also reduce the chances of symptom recurrence.
Understanding the profound impact of conservative care, including the use of orthotic devices, is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes and promoting long-term foot health. Conservative care, specifically the use of orthotic devices, plays a significant role in addressing plantar heel pain and neuropathic symptoms without resorting to invasive interventions.
Preoperative Planning Importance
Proper preparation before surgery is essential for successful outcomes. Assessing risks, preparing the patient, and setting clear expectations are key aspects of preoperative planning. Thorough planning not only ensures optimal surgical results but also includes discussions on postoperative care and recovery.
Understanding the significance of preoperative preparation plays a critical role in the overall success of the surgical procedure. Incorporating these elements into the planning process can lead to better patient experiences and improved treatment outcomes.
Surgical Management of Plantar Fasciitis and Neuropathy
Performing appropriate releases to address nerve entrapment issues like tarsal tunnel syndrome and baxter’s nerve is crucial for surgical management. Postoperative care following heel spur resection involving the abductor hallucis muscle and flexor digitorum brevis is essential. Gait analysis can aid in assessing the impact of surgery on ambulation.
Monitoring for complications such as stress fractures or severity of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis is necessary for optimal outcomes.
Surgical interventions may involve decompression of the posterior tibial nerve at the flexor retinaculum near the medial ankle, specifically targeting the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve, also known as Baxter’s nerve.
Performing Appropriate Releases
Performing appropriate releases in surgical procedures entails precise cutting of constricting tissue bands responsible for pain. Surgeons meticulously identify and release compressed nerve structures to alleviate pressure and facilitate nerve function restoration.
The success of these techniques hinges on skillful execution tailored to the specific underlying condition. Ensuring the selection of the right release technique is paramount in achieving favorable surgical outcomes, emphasizing the importance of expertise and precision in these delicate procedures.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Following surgery for foot conditions like tarsal tunnel syndrome and plantar fasciitis, postoperative care is crucial for pain management and healing promotion. Patients are guided on wound care and prescribed rehabilitation exercises tailored to their needs.
The recovery timeline varies depending on the type of surgical intervention. Physical therapy is essential for reinstating foot functionality post-surgery. It’s imperative to grasp and follow the postoperative care instructions diligently to facilitate a smooth recovery process.
Coping with Plantar Fasciitis and Neuropathy
Seeking ways to cope with plantar fasciitis and neuropathy involves incorporating lifestyle adjustments. Supportive footwear can alleviate discomfort, while ice packs offer relief for acute symptoms. Managing weight can help reduce pressure on the feet, promoting improved mobility. Empowerment comes from understanding the conditions and their effective management strategies. Social support plays a crucial role in navigating the challenges, encouraging proactive engagement in self-care routines.
Is there a cure for Plantar Fasciitis and Neuropathy?
While not all cases find a permanent cure, effective management can enhance quality of life. Surgery targets underlying issues but doesn’t guarantee a cure. Prevention and early treatment are crucial for long-term pain control. Managing symptoms successfully is vital.
What are the first signs of neuropathy in your feet?
The initial indications of neuropathy in your feet may manifest as tingling or numbness, a burning sensation, sharp pain, alterations in foot temperature, or heightened sensitivity to touch. If these symptoms arise, seek medical assessment promptly for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
What are Symptoms of Baxter’s Neuritis?
Sharp or burning pain on the inside of the foot characterizes Baxter’s Neuritis. Pain worsens with activity but improves with rest. Additional symptoms include numbness, tingling, and swelling in the affected area, which can be triggered by tight footwear or prolonged standing.
How does neuropathy affect the treatment of plantar fasciitis?
Neuropathy complicates plantar fasciitis treatment by causing nerve-related symptoms such as foot numbness. Customized plans addressing both conditions are essential. Sensory issues from neuropathy can hinder evaluating treatment effectiveness. Healthcare providers must consider neuropathy when devising plantar fasciitis treatment strategies.
Can plantar fasciitis lead to neuropathy or vice versa?
While plantar fasciitis and neuropathy are distinct conditions, they can coexist. Plantar fasciitis affects the foot’s tissue, while neuropathy involves nerve damage. Untreated severe plantar fasciitis may alter gait, potentially leading to neuropathy. Seeking proper medical care is crucial for managing both conditions effectively.

Conclusion
As the understanding of the relationship between plantar fasciitis and neuropathy deepens, so does the potential for more targeted and effective treatments. The journey towards recovery may seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and resources, it is possible to reclaim the joy of movement and freedom from pain. Remember, every step taken towards understanding and addressing your condition is a step towards a healthier, more comfortable life.
In your journey to overcome plantar fasciitis, have you considered exploring the comprehensive reviews at theheelgp.com to find the treatment that resonates with your needs?
I hope you have found this blog helpful and please feel free to comment and share.
Thanks for reading!
 | Tracy J. Founder, The heel GP |