Plantar Fasciitis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a medical term for the inflammation of the plantar fascia, which is a thick band of connective tissue that runs along the bottom of your foot. One of the main symptoms of this condition is tenderness, which can be quite painful and affect your daily activities. In this post, we will help you understand Plantar Fasciitis, its tenderness, and how it affects your body. We will also discuss the causes and risk factors associated with this condition along with its primary symptoms. Our expert guide will take you through the diagnostic processes used to identify Plantar Fasciitis and available treatments such as nonsurgical and surgical options. Lastly, we will also list some home remedies and lifestyle changes that you can make to manage the tenderness caused by Plantar Fasciitis and prevent it from recurring in the future.
Understanding Plantar Fasciitis and Its Tenderness
Plantar fasciitis occurs due to overuse, impacting the ligament that supports the arch of your foot. The resulting inflammation of the plantar fascia can cause pain and tenderness, especially during the first steps in the morning. This condition commonly leads to heel pain and is influenced by activities like high-impact exercises and tight calf muscles. Understanding these factors contributes to effectively managing plantar fasciitis and its tenderness.
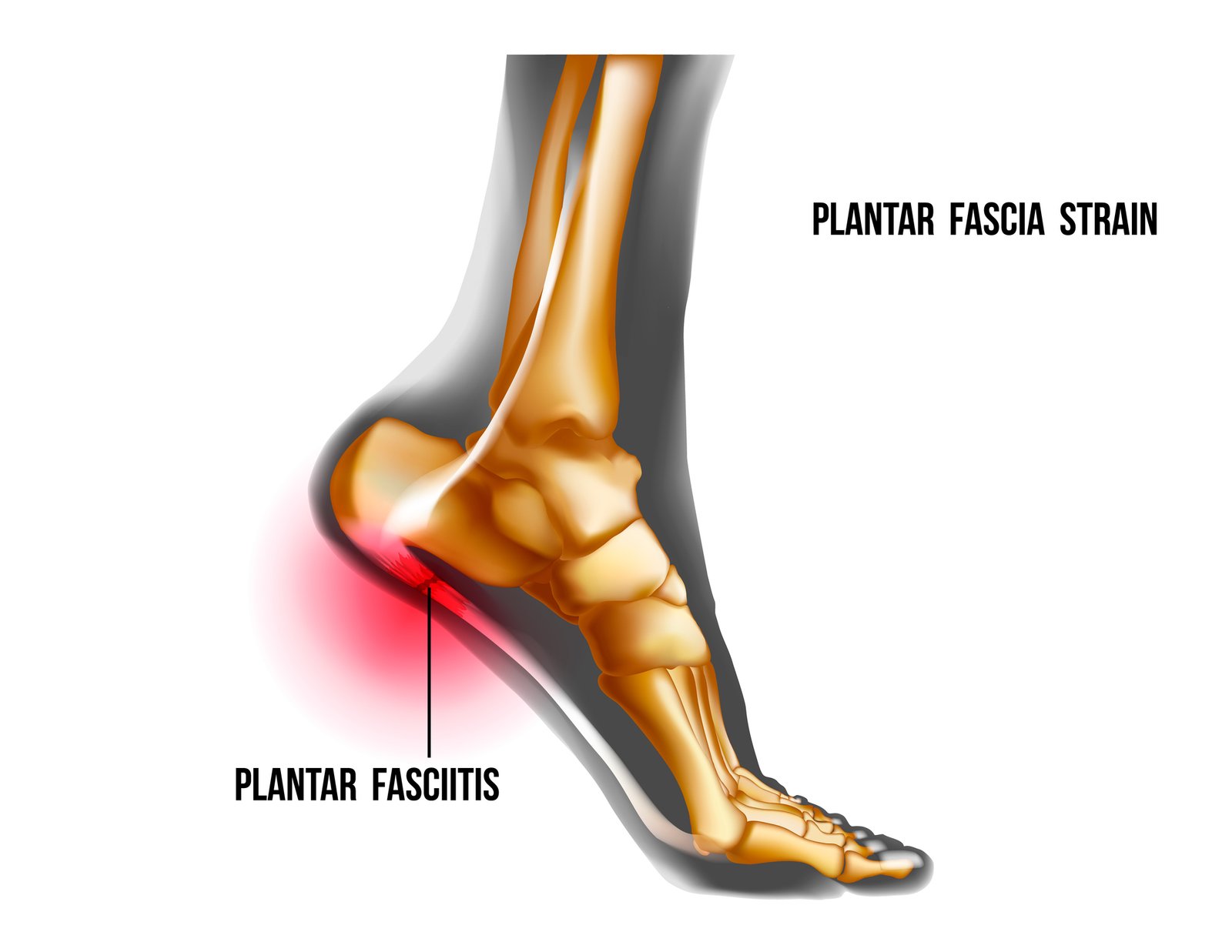
The Anatomy Involved in Plantar Fasciitis
The plantar fascia, a robust band of tissue, extends from the heel to the front of the foot, absorbing and releasing stress during movement. Pain associated with plantar fasciitis is commonly localized at the bottom of the heel and the arch of the foot, caused by straining and tiny tears in the plantar fascia. Tightness in the calf muscles can also lead to increased stress on the plantar fascia, resulting in discomfort.
An Overview of Plantar Fasciitis Tenderness
Experiencing a stabbing pain at the bottom of your foot, especially in the morning, is common with plantar fasciitis. The condition involves small tears in the plantar fascia, leading to tenderness and soreness in the heel and arch of the foot. Prolonged standing or walking on hard surfaces can exacerbate the tenderness, causing discomfort. These symptoms often require assessment by a primary care doctor or a physical therapist for effective management.
How common is plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis, a prevalent cause of heel pain, affects millions annually, especially athletes and runners. Its prevalence in the general population is about 10%, often leading to heel pain at some point in individuals’ lives, particularly among middle-aged individuals and athletes. This widespread foot condition underscores the need for awareness and proactive measures for preventing and managing plantar fasciitis.

Causes and Risk Factors of Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis typically results from overuse, high or flat arches, and prolonged standing or running. Risk factors include obesity, long-distance running, and improper footwear. Age, occupation, and foot structure are also significant contributors. Additionally, muscle tightness, faulty foot mechanics, and specific activities can aggravate the condition, leading to chronic pain and discomfort. Understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Common Causes
Plantar fasciitis often results from overuse, faulty foot mechanics, and high-impact activities. Prolonged standing, walking, or running can cause pain, as can inadequate footwear and tight calf muscles. Repetitive stress on the plantar fascia band of tissue can lead to irritation and pain. Understanding these common causes is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Risk Factors Contributing to Plantar Fasciitis
Risk factors for plantar fasciitis are varied and can include obesity, tight calf muscles, and prolonged periods of standing. Certain professions, such as teaching and healthcare, have been associated with an increased risk of developing the condition. Foot structure also plays a role, with flat feet, high arches, and abnormal foot mechanics being potential contributors. Additionally, age and engaging in physical activities like running can elevate the risk of experiencing plantar fasciitis. Wearing shoes with inadequate support or being on an unsupportive work surface may also lead to the development of plantar fasciitis.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
Recognizing the symptoms of plantar fasciitis is essential. The condition manifests as pain in the bottom of the heel or the arch of the foot, especially after periods of inactivity. Intense pain is often felt during the first steps in the morning, described as stabbing, aching, or burning. Additionally, the pain can radiate from the bottom of the heel to the arch of the foot, indicating the possibility of plantar fasciitis.

Primary Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
The primary symptoms of plantar fasciitis entail discomfort in the bottom of the heel and the arch of the foot. This pain is typically more acute in the morning or after extended periods of inactivity. Individuals may experience stabbing pain, soreness, or tenderness in the foot, along with aching feet after prolonged standing or walking. This can cause difficulty in performing daily activities.
How Pain and Tenderness Manifest in Plantar Fasciitis
Pain in plantar fasciitis often presents as a sharp, stabbing sensation in the heel, sometimes radiating to the arch of the foot. Tenderness can cause discomfort or aching in the foot’s arch, especially after prolonged inactivity. The soreness is typically felt in the heel and arch, impacting daily activities. This chronic pain often prompts individuals to seek assistance from a physical therapist or their primary care doctor.
Diagnostic Processes for Plantar Fasciitis
When diagnosing plantar fasciitis, a doctor performs a physical exam and discusses symptoms. Imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans confirm the diagnosis. Checking for tenderness in the heel bone or bottom of the foot is crucial. Identifying symptoms like stabbing pain in the heel and examining any pain in the plantar fascia area are part of the diagnostic process. This helps in understanding the cause and extent of the condition.
Doctor Examination and Tests for Plantar Fasciitis
During a doctor’s examination for plantar fasciitis, medical professionals may identify tenderness in the plantar fascia or heel, indicative of this condition. Sound waves could be utilized to detect small tears in the foot, a common symptom of plantar fasciitis. Additionally, evaluating the foot for stabbing pain during the initial steps taken in the morning and checking the bottom of the heel for symptoms are essential parts of the examination process.

Importance of Imaging Tests in Diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis
Imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, provide detailed insights into the heel bone and plantar fascia, aiding in diagnosing plantar fasciitis. They help identify symptoms like tiny tears in the plantar fascia and bone spurs, leading to effective diagnosis and treatment. X-rays also offer a closer look at the arch of the foot, providing essential information about plantar fasciitis symptoms and facilitating accurate diagnosis.
Available Treatments
When addressing plantar fasciitis, nonsurgical treatments like physical therapy and night splints offer pain relief. Steroid injections can alleviate soreness, while severe cases may require surgical options like gastrocnemius recession. Overall, the goal of treatment is to reduce pressure on the plantar fascia to alleviate pain, and nonsurgical methods combined with supportive shoes are often effective. This holistic approach helps patients manage chronic pain effectively.
Nonsurgical Treatments and Their Effectiveness
When dealing with plantar fasciitis tenderness, nonsurgical treatments can be highly effective. Physical therapy involves exercises to strengthen lower leg muscles, reducing pain. Night splints are also effective in reducing pain in the plantar fascia, a common symptom of the condition. Supportive shoes play a significant role in alleviating pain in the plantar fascia, addressing the primary symptom of plantar fasciitis. Additionally, a healthy diet contributes to overall foot health, complementing nonsurgical treatment methods.
Surgical Treatments: When Are They Needed?
When nonsurgical methods fail, surgical treatments may be recommended for plantar fasciitis. Gastrocnemius recession surgery can relieve pressure on the plantar fascia, reducing pain. Open surgery is considered when nonsurgical options don’t alleviate symptoms. These treatments aim to reduce severe pain in the plantar fascia area and are recommended for those experiencing significant foot pain.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Living with plantar fasciitis involves implementing effective home remedies like applying ice for relief and making lifestyle changes to reduce pain, focusing on reducing soreness in the plantar fascia. Managing plantar fasciitis tenderness requires simple treatment methods such as calf muscle stretches, aiming to alleviate tenderness in the plantar fascia area. Embracing these home remedies and lifestyle changes can help ease the discomfort associated with plantar fasciitis.

Effective Home Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis tenderness can be alleviated by applying ice to the painful area, reducing soreness and discomfort. Stretching the calf muscles helps in relieving pain in the plantar fascia, a common symptom of this condition. Elevating the foot can effectively reduce tenderness, offering relief from discomfort on the plantar fascia. Additionally, using shoe inserts provides support and relief from the pain associated with plantar fasciitis.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Plantar Fasciitis Tenderness
Managing plantar fasciitis tenderness requires strategic lifestyle adjustments. Wearing supportive shoes and avoiding walking barefoot on hard surfaces can provide relief by reducing pressure on the plantar fascia area, minimizing pain. Additionally, managing tight calf muscles is crucial to ease soreness in the front of your foot. These lifestyle changes can effectively alleviate chronic pain associated with plantar fasciitis.
Prevention Strategies for Plantar Fasciitis
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the plantar fascia, preventing plantar fasciitis. Supportive shoes alleviate pain in the arch of your foot. Regular calf muscle stretches aid in preventing plantar fasciitis pain. Avoid long periods of standing on hard surfaces to prevent soreness. A healthy diet promotes overall foot health, helping avoid plantar fasciitis. Preventing recurrence is key to managing chronic pain.
Can You Prevent Plantar Fasciitis from Recurring?
Preventing the recurrence of plantar fasciitis is possible by understanding the risk factors involved. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises, wearing supportive shoes with orthotic inserts, managing body weight, and avoiding long periods of standing on hard surfaces are essential in preventing plantar fasciitis from coming back.

How long does it take to recover?
Recovery time for plantar fasciitis varies depending on severity and treatment. Mild cases may resolve within weeks, while severe cases can take up to a year or more to heal. Treatments include rest, exercises, therapy, orthotics, and surgery in rare cases. Early intervention and consistent treatment speed up recovery.
How can I tell if my heel pain is due to plantar fasciitis?
Heel pain can be a symptom of plantar fasciitis. If you experience pain in your heel or arch, especially in the morning or after walking or standing for long periods, it could be plantar fasciitis. Tenderness and inflammation near the heel may also be present. A doctor can diagnose this condition through a physical exam and imaging tests if needed.
Can certain shoes or activities aggravate this foot condition?
Certain footwear and activities can aggravate the tenderness associated with plantar fasciitis. It is advisable to avoid high heels, flip flops, and shoes with poor arch support. Activities that put stress on the feet, like running or standing for long periods, can also worsen the condition. Wearing supportive shoes and engaging in low-impact activities can help alleviate symptoms.

Conclusion
In conclusion, it is crucial to understand the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic processes of plantar fasciitis tenderness. By recognizing the risk factors and taking preventive measures, you can reduce the likelihood of developing this condition. In the event that you do experience plantar fasciitis, there are various treatment options available, both nonsurgical and surgical, depending on the severity. Additionally, incorporating home remedies and making lifestyle changes can help manage the pain and discomfort associated with plantar fasciitis. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. By prioritizing your foot health and taking proactive steps, you can alleviate plantar fasciitis tenderness and improve your overall well-being.